A popular format to import into a Pandas dataframe is CSV. It stands for Comma Separated Values but the values can also be separated by other delimiters like the semicolon. Tricky about working with these files can be the format of dates and decimal numbers. Let’s see how we can import a files like this using the Month/Day/Year date format:

To import a CSV file you use the read_csv() function and specify the separator using the sep argument. Casting the numeric and date columns to the correct type can be done using the to_datetime() and to_numeric() functions. Watch out though for the comma as thousand separator, Pandas can’t handle that correctly.
import pandas as pd
import os
# get current folder
path = os.getcwd()
# load csv file into DataFrame
dfOrders = pd.read_csv( fr'{path}\..\..\Data\Orders.csv', sep=';')
# Convert Text to DateTime, Numeric
dfOrders['OrderDate'] = pd.to_datetime( dfOrders['OrderDate'], format='%m/%d/%Y' )
dfOrders['Price'] = pd.to_numeric( dfOrders['Price'].str.replace(',', '') )
# Calculated Columns
dfOrders['LineTotal'] = dfOrders['Quantity'] * dfOrders['Price']
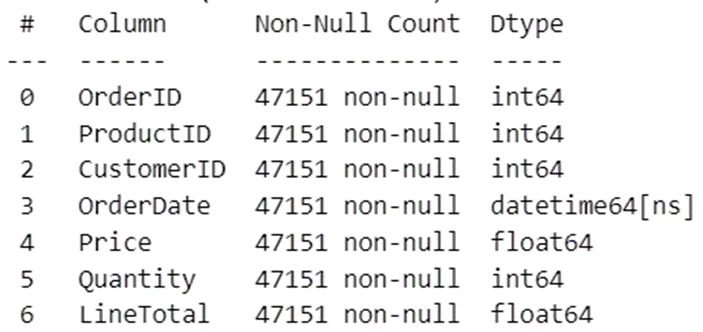
dfOrders.info()
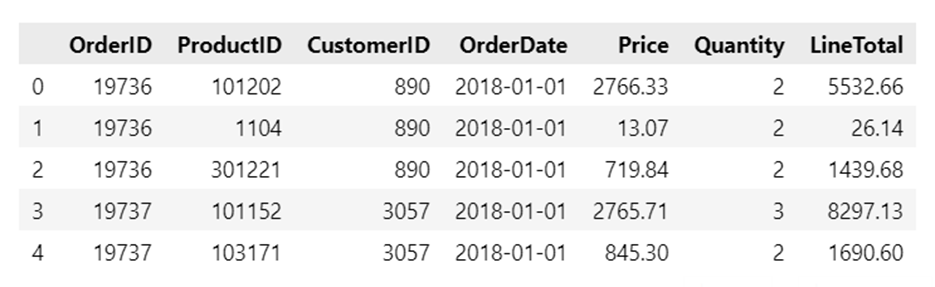
display(dfOrders.head(5))